Last updated on
Exploring sanitary plumbing fittings becomes an enthralling journey because of their hidden roles in safeguarding our health and comfort in the home.
Sanitary plumbing fittings are integral components in any plumbing system, designed to ensure the smooth and hygienic transportation of water. They include a variety of devices such as pipes, faucets, valves, and connectors that work together to prevent contamination of the water supply by keeping waste and clean water separate.
These fittings play an essential role in both residential and commercial plumbing systems, ensuring that water flows efficiently and safely. This article will delve into the different types of sanitary plumbing fittings, their functions, and how to choose the right ones for your specific needs.
So, whether you’re planning a home renovation or just curious about plumbing, keep reading for detailed insights.
Key takeaways:
- Sanitary plumbing fittings ensure hygienic water transportation and prevent contamination.
- Types include elbows, tees, crosses, reducers, flanges, plugs, caps, and valves.
- Materials include stainless steel, PVC, brass, and copper, each with unique advantages.
- Fitting sizing is determined by inside/outside diameter, schedule numbers, and tubing size.
- Connection types include welding, threads, clamp ends, push-fit, and flanging.
Table of Contents
Sanitary Fitting Types
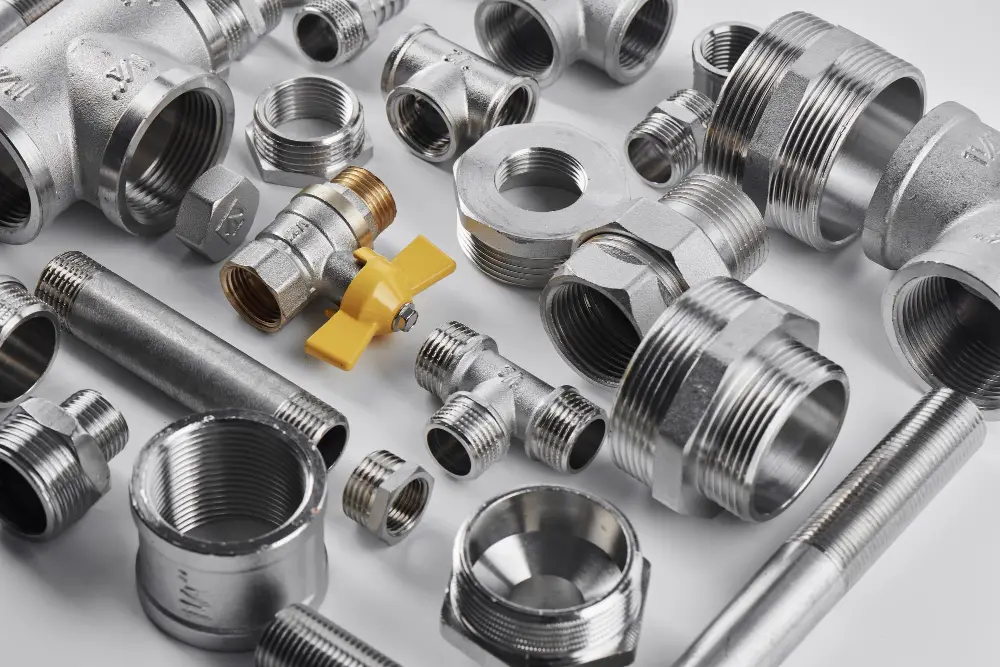

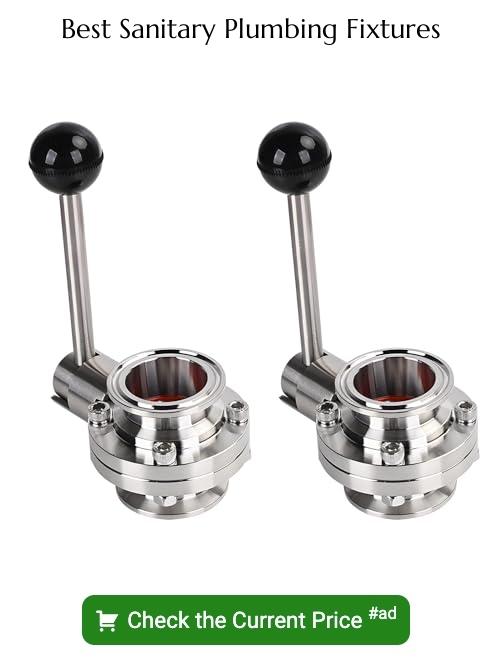
Sanitary fittings come in several categories, mainly based on their design features. Elbow fittings, a common type, allow for a change in pipe direction, typically available in 45 and 90 degree angles. Tee fittings split or combine flow, ideal for connecting pipes of different diameters or diverting the water flow.
Cross fittings have four openings in four directions. These serve as a junction point for four pipes. Reducer fittings connect two pipes of differing sizes, having a varying diameter at each end. Flange fittings, used in high-pressure scenarios, enable pipes to connect to each other or to a valve or other equipment.
Plug and cap fittings shut off the pipe end, used when the pipe needs to be blocked or ended. Finally, valves control fluid flow and pressure, with multiple types including ball, globe, gate, plug, butterfly, check, and pressure relief valves.
Understanding the right type of fitting to use is integral to creating an efficient sanitary plumbing system. Do remember, each fitting has its unique purpose and functionality.
Material Selection for Sanitary Plumbing Fittings
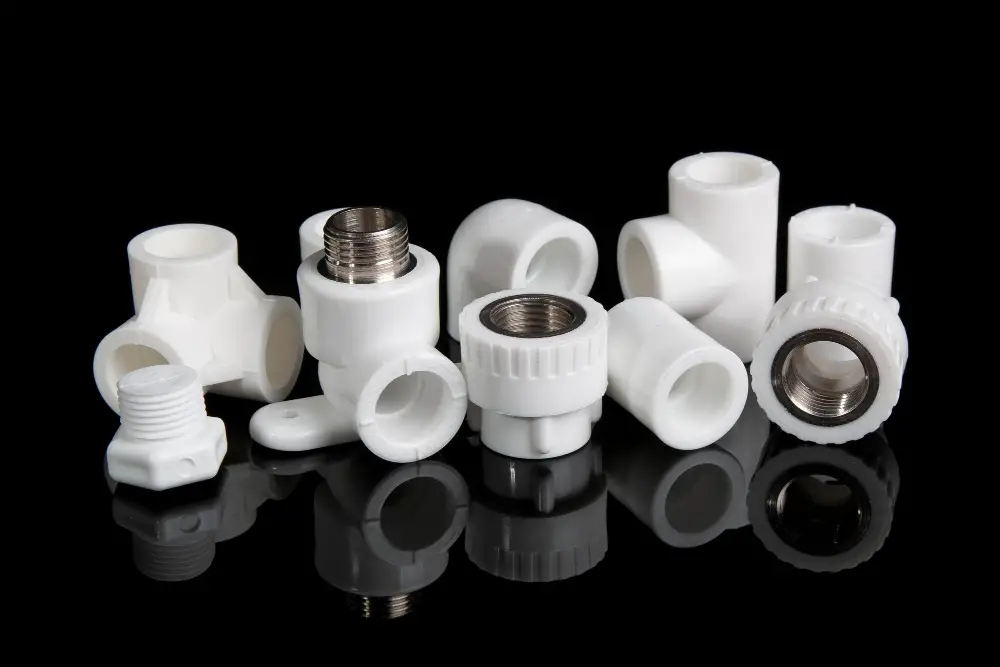

Choosing the perfect material for sanitary fittings is crucial. It impacts both the durability and hygiene of the entire plumbing system.
Stainless steel is considered an industry standard due to its superior resistance to corrosion and extreme temperatures. It’s hardwearing, low maintenance, and can remain sanitary over time.
PVC or plastic is another common choice due to its affordability and versatility. It’s especially popular for installations that require water resistance and non-conductive properties. However, PVC is not as long-lasting as its steel counterpart.
Brass is popular for its robust and corrosion-resistant nature, often used in high-temperature and high-pressure environments. One caveat, though, is that it may contain a trace amount of lead, something to consider for strict health and safety regulations.
Copper, known for its unparalleled thermal conductivity, is commonly used in heated water applications. Users should note that it’s prone to corrosion in acidic environments.
Each material comes with unique advantages and potential downsides. It’s important to assess all factors, such as durability, cost, ease of installation, maintenance, and specific use, when deciding on suitable sanitary fittings for any plumbing project.
Sanitary Pipe Fitting Sizing

The size of sanitary plumbing fittings is measured by either their inside diameter (ID) or outside diameter (OD). Sizing can vary between different pipe fitting types but are generally categorized into standard nominal pipe sizes (NPS).
1. Nominal Pipe Size (NPS): This indicates the approximate inside diameter of the fitting. A common misconception is that NPS measures the outside diameter; however, this is not the case. For instance, an NPS 1 fitting means its approximate inside diameter is 1.05 inches.
2. Outside Diameter (OD): This measurement refers to the exact diameter of the outside of the pipe or fitting. Crucial for sanitary fittings as it ensures a tight, secure connection among components.
3. Schedule Numbers: These are used to describe the thickness of the pipe wall, which corresponds directly to the interior diameter. Higher schedule numbers point to thicker walls.
4. Tubing Size: Unlike pipes, sanitary tubing is measured by the exact outside diameter and the wall thickness. Tubing is often used in applications where corrosion resistance and cleanliness are critical.
Understanding these sizing concepts is integral in creating an efficient and effective sanitary plumbing system. Incorrect sizing can cause major issues, like leakage or blockage. Therefore, picking the right size demands precise calculations considering the type and amount of fluid that will flow through it.
Connection Types for Sanitary Fittings
Various methods are employed to connect sanitary fittings, crucial to ensuring leak-free and efficient installations.
1. Welding: One of the most secure ways to join fittings, often used in industries where hygiene is paramount. This eliminates the need for sealants that can harbour bacteria.
2. Threads: Threaded connections require a male and female ending, often sealed with plumbing tape or compound. While convenient, threads can create spots for bacteria to collect.
3. Clamp ends: This is a versatile method allowing easy assembly and disassembly, ideal for systems that require regular cleaning.
4. Push-fit: For effortless and quick installations, push-fit connections are great. They use a rubber seal to create a water-tight connection.
5. Flanging: This involves attaching flanges to the pipe ends and connecting them with bolts, providing a strong and reliable joint but requiring accurate alignment.
Each method has pros and cons, and choosing the right one depends on factors such as the application, hygiene requirements, and plumbing design.
Cleaning Ease of Sanitary Fittings

When considering ease of cleaning, sanitary fittings excel. Designed with smooth, non-porous surfaces and minimum dead legs (areas where fluid can become stagnant), they are crafted to thwart bacterial growth and biofilm development. Handy sweeping elbows and tees render pipe interiors fully visible for easy inspection and cleaning.
To maintain hygiene, often a two-step process is practiced. First, a rinse to remove the bulk of residues followed by a scrubbing or a cleaning-in-place (CIP) process. Involving circulation of cleaning liquids such as hot water, sodium hydroxide, or nitric acid solutions, CIP is a common technique in the food, dairy, and beverage industries. Alternatively, a steam-in-place (SIP) method, employing high temperature steam, is also utilized to sterilize the fittings.
To further enhance cleaning potential, manufacturers have even started to offer removable fitting systems. These can be easily disassembled and cleaned individually, ensuring thorough sanitation. It’s essential, however, to remember that any cleaning regimen should be strictly in accordance with the fitting material to prevent any potential damage or degradation.
Lastly, a concept that enhances cleaning ease is the use of FDA-compliant seals in the fittings, which helps ensure that substances do not leak or flow in unintended directions, maintaining the cleanliness and integrity of the system.
Sanitary Tube Fittings and Their Significance

For industries that place high importance on cleanliness and hygiene—like the food and beverage, biopharmaceutical, or cosmetic sectors—tube fittings play a critical role since they are responsible for transporting liquid products.
An important reason behind their ubiquity is their smooth, non-absorbent, leakproof properties that do not allow bacteria or other microbes to stick on their surfaces, which helps maintain hygiene standards.
Being easy-to-clean, these fittings also ensure the carried substance retains its original characteristics with no contamination.
Additionally, they are designed to handle a wide range of pressure and temperature conditions, further making them an optimal choice for sanitary applications.
Besides, their credibility can be judged from the fact they meet the stringent 3-A standards for tube fittings—a protocol recognized internationally for its sanitation performance criterias.
It emphasizes that no shortcuts have been taken in the creation of a safe, sterile environment, thereby ensuring that the public’s health is the foremost priority.
Their specialty also lies in their connection systems, which permit easy setting and removal, facilitating maintenance operations while complying with safety standards.
Thus, they play a pivotal role in the seamless working of sanitary plumbing systems while promoting health and safety standards.
A Standards for Tube Fittings
To ensure the safety and hygiene of sanitary fittings, the 3-A Sanitary Standards are observed. These standards are a set of criteria for the design and fabrication of equipment that comes into contact with food or other hygiene-sensitive processes. They were originally established in the 1920s by dairy processors looking to ensure safe and sanitary processing conditions.
A key aspect of these standards pertains to the surface finish of tube fittings, specifications mandate a specific level of smoothness as rough or uneven surfaces can harbor bacteria. Also, all pipe fittings have to be free from cracks, crevices or joints where impurities can be trapped.
Materials used must resist corrosion and withstand chemical reactions with cleansing and sanitizing agents. The stainless steel in Grades 304 or 316 is the material of choice, relationships with these conditions.
Standards require fittings to be accessible and readily dismantlable for inspection, cleaning or maintenance. Tube fittings with 3-A standards certification indicate adherence to these quality control methods, contributing to hygienic and reliable plumbing installations.
Usage of Sanitary Plumbing Fittings in Different Industries

Within the food and beverage industry, sanitary fittings play a pivotal role in ensuring food hygiene and safety. They facilitate easy cleaning of the system to eliminate any bacterial contamination hazards. In dairy processing, fittings also need to withstand high temperatures and pressure conditions during pasteurization.
Pharmaceutical manufacturing, too, necessitates stringent hygiene standards, with high-grade stainless steel often being the material of choice for sanitary fittings. Such fittings should meet requirements for chemical resistance, smooth internal surfaces, and negligible fluid retention to ensure safe, clean manufacturing processes.
Last but not least, water treatment plants use sanitary fittings versatilely, from piping for water purification processes to sewage treatment applications. Not only do these fittings need to be corrosion-resistant, but they also have to be robust enough to withstand the potential harsh conditions of waste treatment.
Micro-breweries also significantly leverage the use of sanitary fittings. These fittings play a vital role in the brewing and fermentation processes, largely owing to their resistance to temperature variations and chemical interactions. Molded parts, specifically, are favored for their leak-proof properties.
Provided these examples, sanitary fittings serve a multitude of industries – each with its unique requirements and standards. Though these fittings may seem inconsequential, their role in contributing to overall industry hygiene, safety, and productivity is undeniable.
FAQ
What is the difference between sanitary fittings and plumbing fittings?
Sanitary fittings are distinguished from regular plumbing fittings primarily by being made from stainless steel, a material that facilitates easy cleaning and disinfection, while ordinary fittings are typically made from materials like iron, copper, or aluminum.
What is an example of a sanitary fitting?
An example of a sanitary fitting is a water closet.
What are the types of sanitary fittings?
The types of sanitary fittings used in buildings include hand wash basins, sinks (glazed or stainless-steel), bath tubs, and water closets.
How do sanitary fittings work?
Sanitary fittings function by structurally reducing areas of potential entrapment, thereby diminishing the chances for bacteria to accumulate.
Which materials are sanitary fittings typically made from?
Sanitary fittings are typically made from stainless steel, brass, plastic, or copper.
How should sanitary fittings be maintained for longevity and hygiene?
Sanitary fittings should be maintained for longevity and hygiene by regular cleaning with non-corrosive, mild cleaning agents, swift repair of leaks to prevent rusting, avoiding over-tightening of fittings to prevent wear and tear, and proper ventilation to deter fungal growth.
How can one determine the quality of a sanitary fitting?
The quality of sanitary fittings can be determined by checking the material used, examining for smooth operation, ensuring no leakage, and verifying adherence to industry standards.





